Django CRUD and Forms
- CRUD: create, retrieve, update, delete.
- Django forms provides a framework that allow users to define forms and fields programmatically.
Regular HTML forms:
<form action="/team_name_url/" method="post">
<label for="team_name">Enter name: </label>
<input id="team_name" type="text" name="name_field" value="Default name for team.">
<input type="submit" value="OK">
</form>
action: where data to be sent for process.
post: use post when data will change in database.
get: use get only when data will not change in database.
Django form handling process
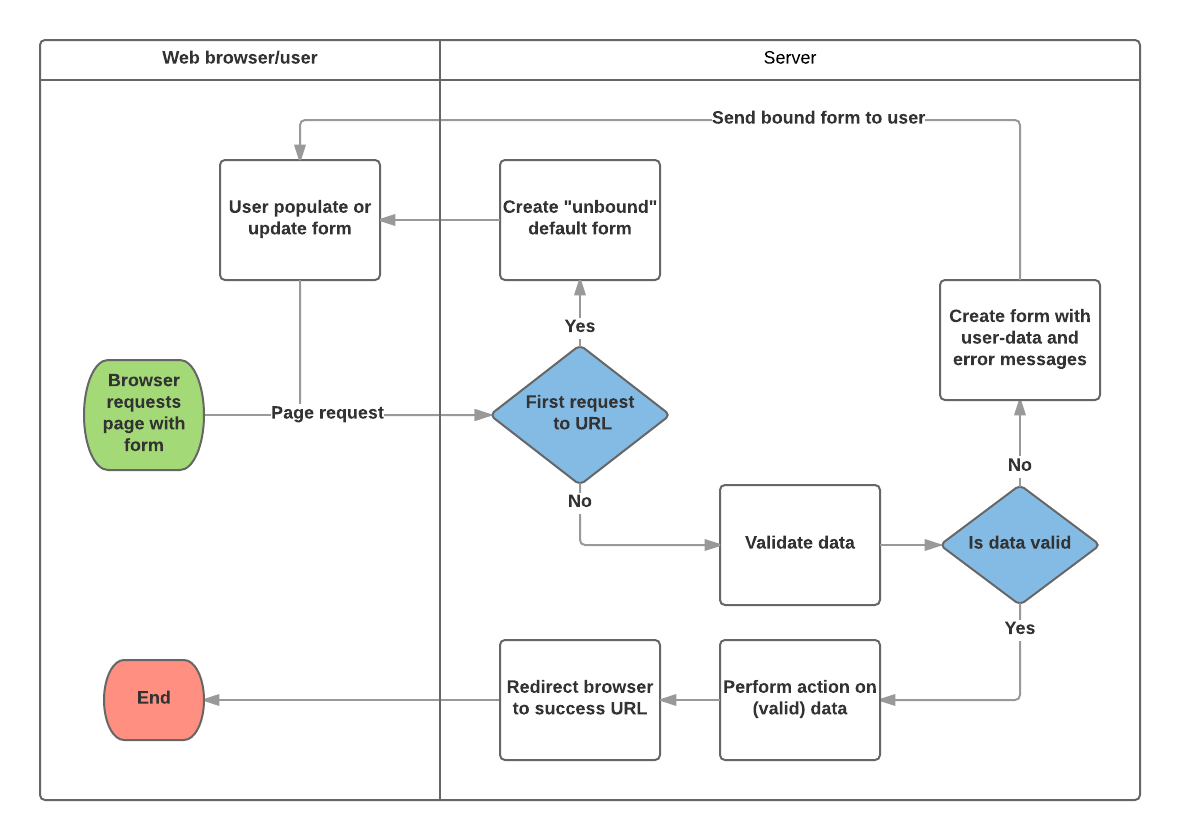
- 1, Display form requested by user
- 2, receive data from a submit request and bind it to the form.
- 3, clean and validate the data.
- 4, if data is invalid, populate errors, re-display form.
- 4, if data is valid, perform the required actions.
- 5, after completion of form redirect user to another page.
Form class
Form class is the key of Django’s form handling system.
"It specifies the fields in the form, their layout, display widgets, labels, initial values, valid values,
and (once validated) the error messages associated with invalid fields. The class also provides methods
for rendering itself in templates using predefined formats (tables, lists, etc.) or for getting the value
of any element (enabling fine-grained manual rendering)."
--MDN web docs
Form fields
Form fields consist of two parts, type and arguments. For example:
forms.DateField(help_text="Enter a date between now and 4 weeks (default 3).")
DataField is type, adn help_text is the arguments. There are many types and each type have similar arguments.
Validation
The easiest way to validate is the method clean_<fieldname>().
URL configuration
URL configuration will redirect URLs to the according functions in views.py.
View
- render the default form, or
- rerender with error message, or
- process data and redirect to new page
Template
use python markup language to render form contents