Forms
- Form Controls
adding text passing input text areae making choices checkboxes dropdown boxes submitting formse image buttons uploading files
- Whenever you want to collect information from visitors you will need a form, which lives inside a
<form>element. - Information from a form is sent in name/value pairs.
- Each form control is given a name, and the text the user types in or the values of the options they selectare sent to the server.
- HTML5 introduces new form elements which make it easier for visitors to fill in forms.
Lists, Tables & Forms
List
- list-style-type
- list-style-image
- list-style-position
- list-style
Table properties
<table><thead><tr><th><td><tfoot>
Table example:
<h1>First Edition Auctions</h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Author</th>
<th>Title</th>
<th class="money">Reserve Price</th>
<th class="money">Current Bid</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>E.E. Cummings</td>
<td>Tulips & Chimneys</td>
<td class="money">$2,000.00</td>
<td class="money">$2,642.50</td>
</tr>
<tr class="even">
<td>Charles d'Orleans</td>
<td>Poemes</td>
<td class="money"></td>
<td class="money">$5,866.00</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>T.S. Eliot</td>
<td>Poems 1909 - 1925</td>
<td class="money">$1,250.00</td>
<td class="money">$8,499.35</td>
</tr>
<tr class="even">
<td>Sylvia Plath</td>
<td>The Colossus</td>
<td class="money"></td>
<td class="money">$1031.72</td>
</tr>
</table>
Styling forms
- styling text input
- styling submit buttons
- styling fieldset and legends
- aligning form
Summary
In addition to the CSS properties covered in other chapters which work with the contents of all elements, there are several others that are specifically used to control the appearance of lists, tables, and forms.
List markers can be given different appearances using the list-style-type and list-style image properties.
Table cells can have different borders and spacing in different browsers, but there are properties you can use to control them and make them more consistent.
Forms are easier to use if the form controls are vertically aligned using CSS.
Forms benefit from styles that make them feel more interactive.
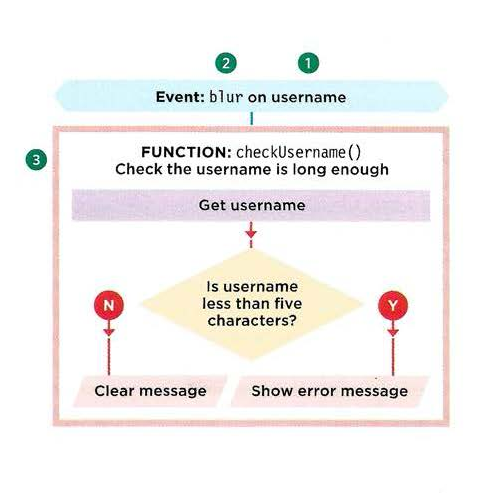
Event
“When you browse the web, your browser registers different types of events. It’s the browser’s way of saying, “Hey, this just happened .” Your script can then respond to these events.”
- Event handling
Select the element node(s) you want the script to respond to.
Indicate which event on the selected nodes will trigger the response.
State the code you want to run when the event occurs.
-
addEventListener()
-
callback function
-
event.preventDefault()
Summary
-
Events are the browser’s way of indicating when something has happened (such as when a page has finished loading or a button has been clicked).
-
Binding is the process of stating which event you are waiting to happen, and which element you are waiting for that event to happen upon.
-
When an event occurs on an element, it can trigger a JavaScript function. When this function then changes the web page in some way, it feels interactive because it has responded to the user.
-
You can use event delegation to monitor for events that happen on all of the children of an element.
-
The most commonly used events are W3C DOM events, although there are others in the HTMLS specification as well as browser-specific events.